Email Address
info@iapaai.com
Email Address
paai.pedsallergy@gmail.com
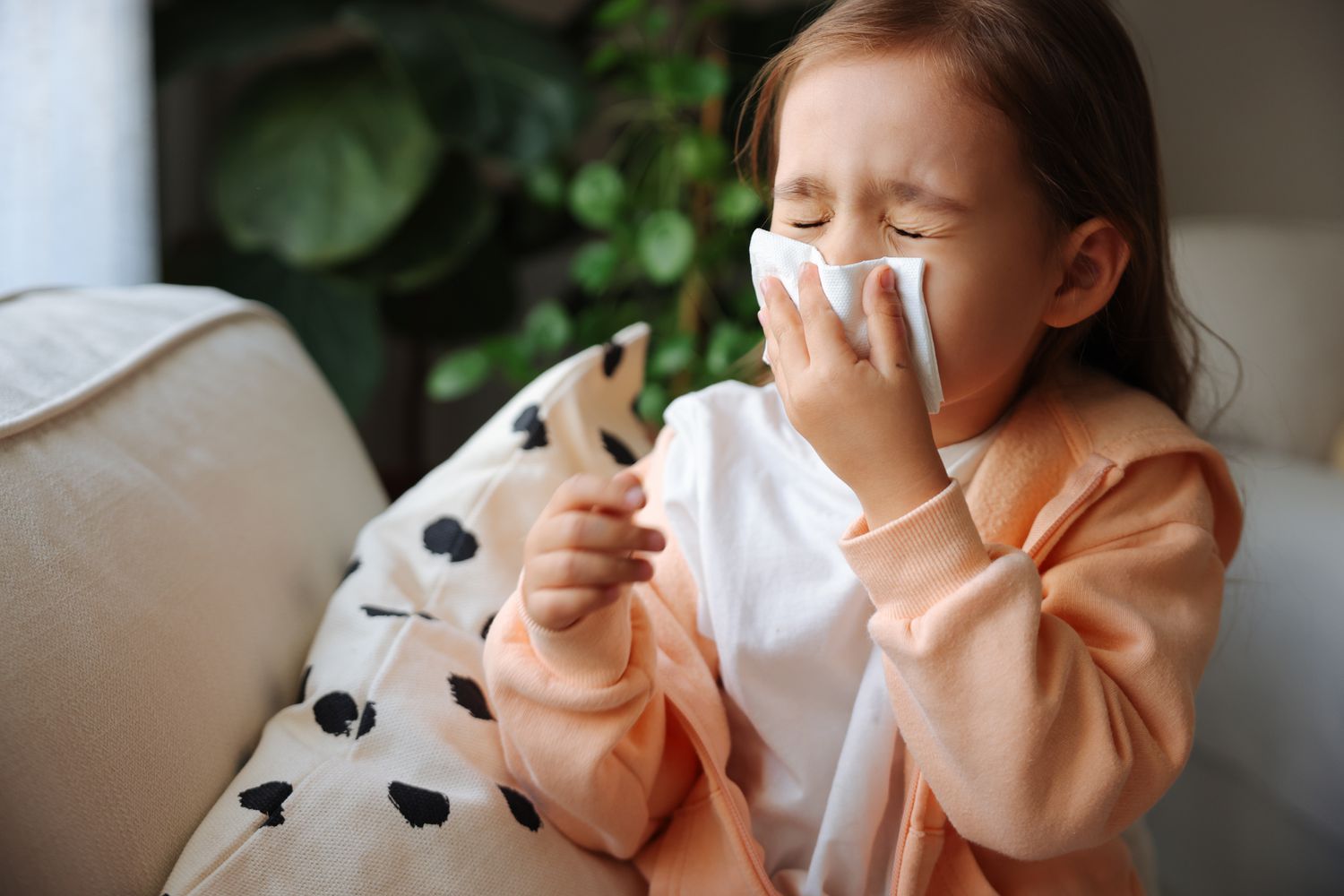

An allergy is an overreaction of the immune system to substances that are generally harmless to most people. These substances are called allergens, and they can include things like pollen, dust mites, mold, pet dander, certain foods, insect stings, or medications. When someone with an allergy comes into contact with an allergen, their immune system mistakenly identifies it as a harmful substance and triggers an immune response. This immune response can cause a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild to severe.
Normally, the immune system protects the body from harmful invaders like viruses and bacteria. However, in people with allergies, the immune system reacts inappropriately to harmless substances. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
The first time an allergic person is exposed to an allergen, their immune system "learns" to recognize it as harmful. The body produces a specific type of antibody called IgE (immunoglobulin E) to respond to the allergen. This process is called sensitization, and it may not cause noticeable symptoms at first.
On subsequent exposures to the same allergen, the IgE antibodies bind to immune cells called mast cells, which are found in various tissues, particularly the skin, lungs, and digestive system. When the allergen enters the body again, it binds to the IgE antibodies on the mast cells, causing them to release histamine and other chemicals
Histamine is a chemical that causes the typical symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as inflammation, itching, swelling, and mucus production. This is what leads to the familiar allergy symptoms.
There are several types of allergies, depending on the allergen involved:
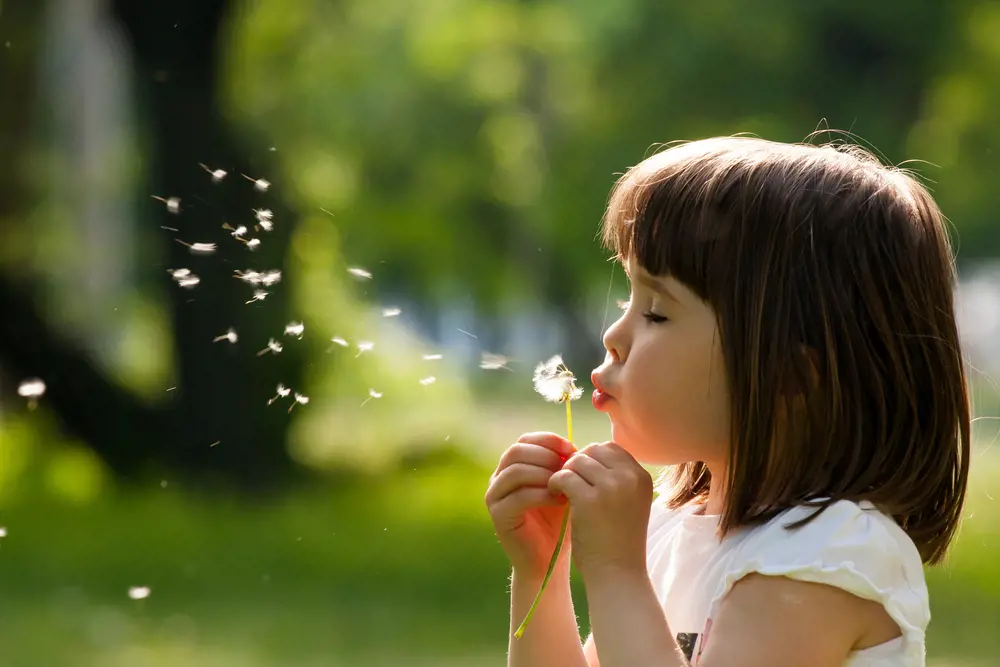

Pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds can trigger sneezing, a runny nose, and itchy eyes.
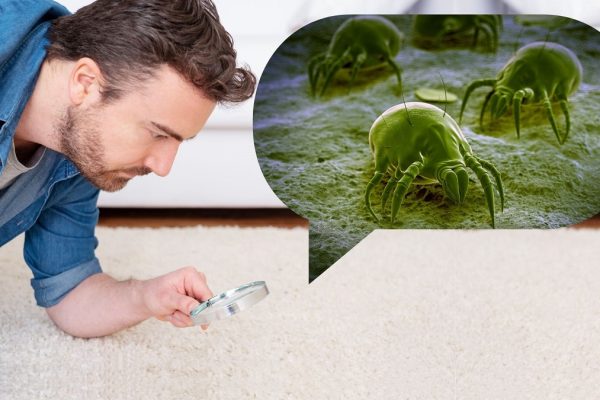

Dust mites and their waste products can cause symptoms like sneezing, nasal congestion, and coughing.
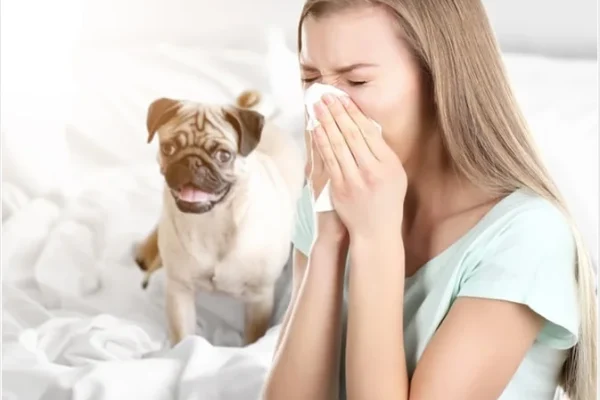

Pet dander (tiny flakes of skin shed by cats, dogs, and other animals) is a common cause of allergic reactions.
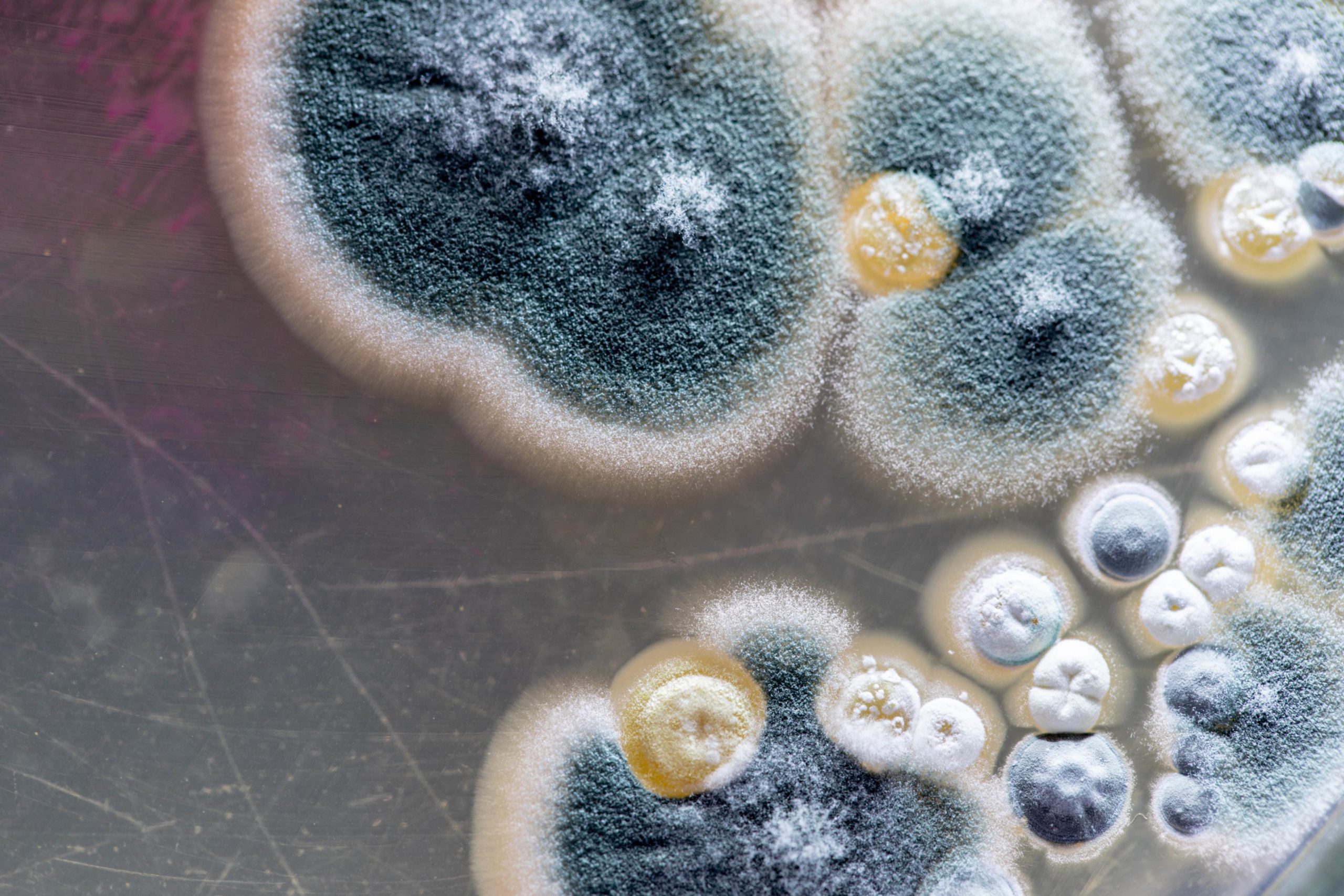
Mold spores can trigger asthma-like symptoms, particularly in damp, humid environments.

Common food allergens include nuts, shellfish, eggs, milk, wheat, soy, and fish. Food allergies can cause symptoms ranging from mild hives or stomach upset to life-threatening reactions such as anaphylaxis, a severe, whole-body reaction.
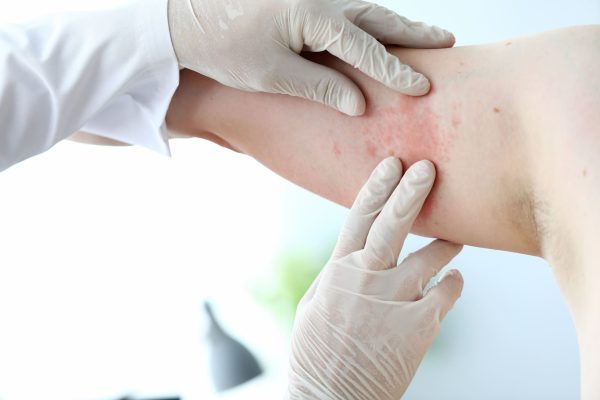
Eczema (atopic dermatitis) is a chronic skin condition that can be triggered by allergens like dust mites, pet dander, or certain foods.
Contact Dermatitis: This occurs when the skin reacts to an allergen like poison ivy, nickel in jewelry, or certain cosmetics, causing itching, redness, and swelling.
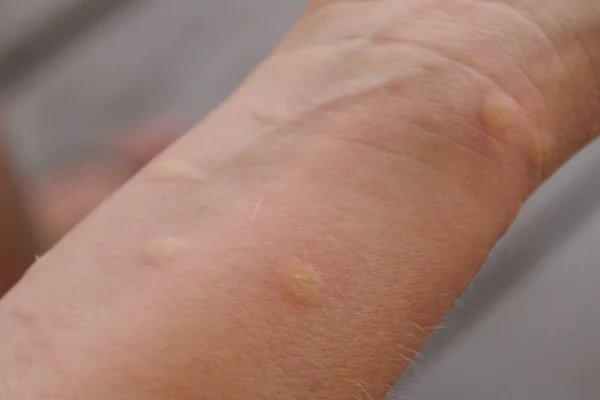
Some people are allergic to insect stings (e.g., from bees, wasps, or hornets). An allergic reaction can range from swelling at the site of the sting to a serious allergic reaction (anaphylaxis).
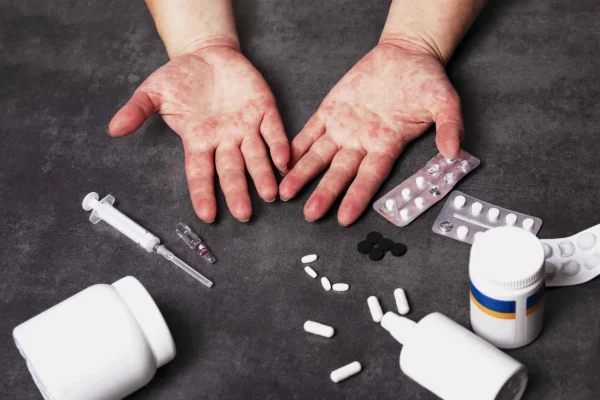
Some people are allergic to certain medications, including antibiotics (like penicillin), aspirin, or sulfa drugs. Reactions can range from mild skin rashes to severe reactions like anaphylaxis.
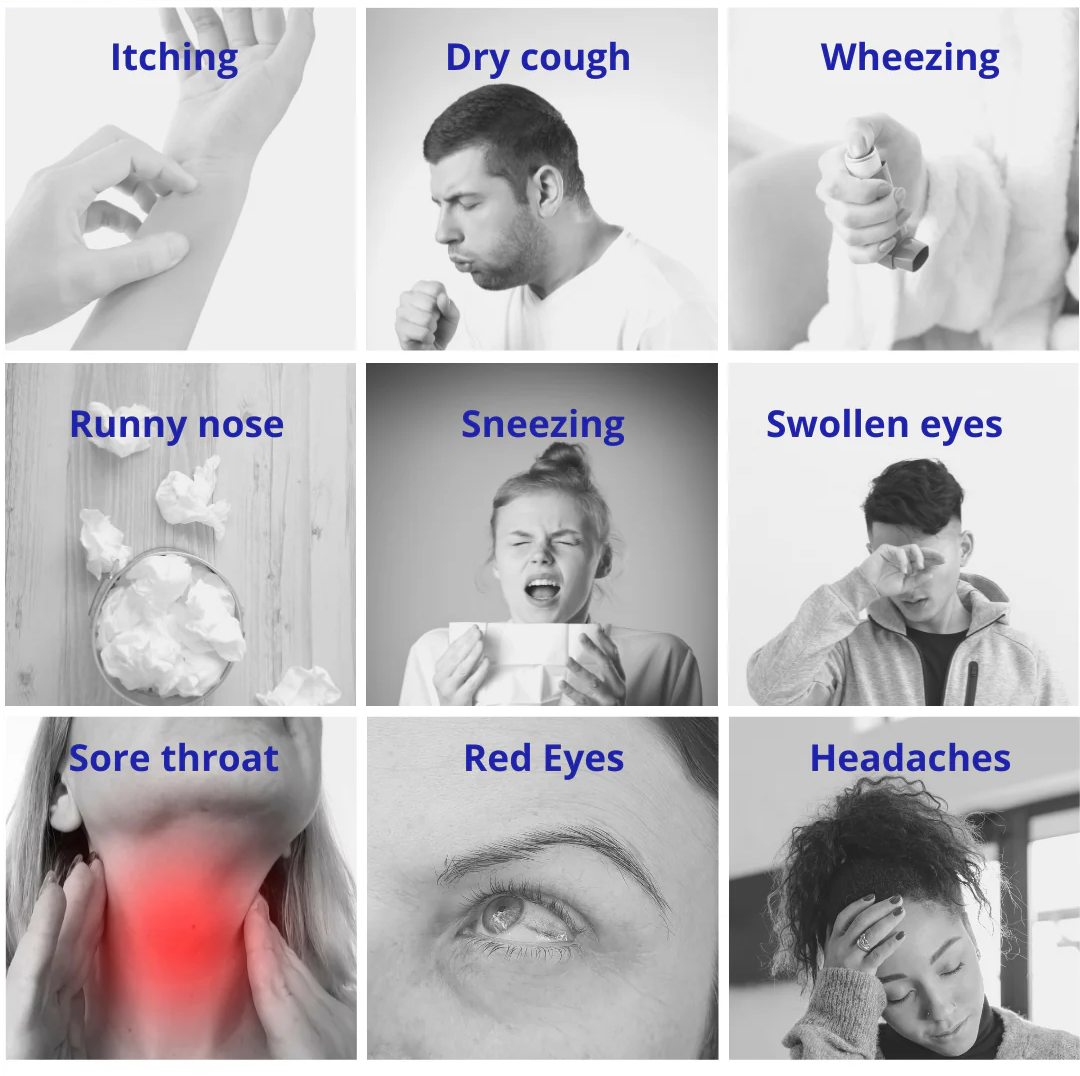
The symptoms of an allergic reaction can vary depending on the type of allergy and the person’s sensitivity, but common symptoms include:
IAP Pediatric Allergy and Applied Immunology Chapter (IAP-PAAI) aims to promote awareness, education, research, and best practices in the field of allergy and asthma. It also works to enhance access to care, provide support to healthcare professionals, and advocate for policies that benefit patients with these conditions.
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved.